SYMPTOMS
Why Is My Dog Limping? Symptoms and Causes of Lameness in Dogs
페이지 정보
본문

What is lameness in dogs?
Lameness in dogs involves impaired limb use due to pain or injury. It can impact one or multiple legs, arising suddenly from trauma or gradually due to chronic conditions. Common causes are soft tissue injury, joint issues, fractures, and hip dysplasia. Puppies to seniors can be affected. Diagnosing and differentiating a dog’s lameness from acute (suddenly) or chronic (persistent) limping to guide treatment options.
Acute vs. chronic limping or lameness in dogs
Chronic lameness:
Chronic lameness lasts over 2 weeks and warrants a vet visit. Gradual onset limps stem from long-term conditions like osteoarthritis or dysplasia. Don't delay appointments; early detection aids treatment effectiveness, especially for bone cancer or hip dysplasia. Osteoarthritis brings morning stiffness, easing with movement and cold or damp weather intensifies it.
Acute lameness:
Acute lameness occurs suddenly, often post-exercise, and may resolve itself within 2 weeks. Suspect cuts, bruises, sprains, or foreign objects. Sudden onset can be linked to injury or trauma, and should be checked out by a veterinarian as soon as possible.
What are the causes of puppy lameness or limping?
Lameness results from a variety of causes from leg injuries or pain in bones, joints, ligaments to certain conditions that affect the nerves, skin, etc. Age and weather can also impact the severity of lameness in dogs. Common causes include trauma, chronic conditions, and various issues categorized as follows:
⦁ Paw injury
Lameness can result from stepping on glass, thorns, or bites from insects/animals. Nail breakage/bruising and burns/frostbite are also culprits for this symptom.
⦁ Trauma
Trauma, like car accidents or sports injuries, can lead to severe lameness due to bone fractures, dislocations, ligament ruptures, joint trauma, and spinal nerve issues. In extreme cases, the leg might not support weight or could be raised.
⦁ Joint disease
Lameness arises from conditions like osteoarthritis, hip and elbow dysplasia, patellar luxation, ligament disease, intervertebral disk disease, and osteochondritis dissecans (OCD). Infections (e.g., Lyme disease) or autoimmune disorders can also trigger joint pain and lameness.
⦁ Bone disease
Puppies of large breeds frequently experience bone abnormalities, including hypertrophic osteoarthropathy and panosteitis, leading to intense pain while walking. Adult to older puppies might encounter bone tumors, notably osteosarcoma.
What are the symptoms of puppy lameness in dogs
Signs of lameness in dogs
⦁ General signs of pain and discomfort, like licking the painful area.
⦁ Avoidance of walking, running, or stairs, and an abnormal gait.
⦁ Difficulty placing feet on the floor.
⦁ Swelling around the joints.
⦁ Decreased muscle mass in the affected leg.
Classification of lameness location
Identify affected leg by observing weight distribution:
Forelimb lameness:
Puppy raises head when affected leg touches floor, lowers with healthy leg. Forelimb stride shorter than hindlimb.
Hind leg lameness:
Dog shifts weight forward, minimizing hind leg use. Tail/hip on affected leg side may lift when that leg touches the floor.
Recognizing emergency symptoms
Be vigilant for these signs that require immediate attention:
⦁ Signs of extreme pain such as behavior changes, leg shaking, and aggression.
⦁ Overt fractures and dislocations
⦁ Bleeding
⦁ Dragging
⦁ Other alarming signs such as lethargy, shortness of breath, high fever, and vomiting.
What is the risk of lameness in dogs?
Several factors increase the risk of lameness in dogs:
Weight impact:
Overweight or obese dogs strain bones and joints, escalating potential issues.
Arthritis in aging dogs:
Older dogs often experience arthritis-related lameness, notably in knees, shoulders, and hips.
Bone abnormalities in puppies:
Large breed puppies can develop bone problems like hypertrophic osteoarthritis or panosteitis.
Genetic factors:
Breeds like Labrador Retrievers and German Shepherds are prone to hip or elbow dysplasia, genetic conditions causing joint deformities.
Home treatments for lameness or limping in dogs

If you notice limping, start by inspecting paws for injuries or pain. Remove foreign objects like thorns, check for wounds, and disinfect. For minor sprains, apply a 15-minute ice pack twice daily till symptoms resolve. Persistent movement can worsen issue, so temporarily limiting exercise can help relieve some of your pet’s pain. Avoid using NSAIDs like aspirin without vet guidance due to potential side effects. Lastly, if limping persists despite rest, seek veterinary attention to diagnose the cause and ensure your pup's well-being.
Diagnosing lameness in dogs

During the hospital visit, the veterinarian might inquire about the following to pinpoint the cause:
⦁ When did the symptoms begin?
⦁ Did it follow trauma?
⦁ Is the lameness constant or worsening with age?
⦁ Have you attempted any home treatments? If yes, what?
⦁ Are there any other health or behavior issues in your dog?
After inquirin gabout your pet’s symptoms, a veterinarian will conduct some of the following tests for diagnosis:
Physical examination:
Gait analysis, sitting, walking observed. Orthopedic and nerve exams assess injury, swelling, warmth, stiffness, and leg movement. Diagnosis through bone and joint palpation may also be considered depending on the certain assessments.
X-ray:
Detects bone and joint issues, fractures, dislocations. CT or MRI for finer imaging.
Additional procedures:
There are other additional examinations that may be considered to diagnose lameness if previous results come inconclusive. Such as joint fluid centesis for arthritis suspicion or biopsy for tumors. Blood tests can help identify any infections or immune diseases like Lyme disease.
Treatment options for lameness in dogs

Treatment for lameness is based on finding the underlying cause. Some dogs may recover with just a few days of rest, but others may require treatment options such as medication or surgery. The prognosis is better if you visit the hospital sooner than later.
NSAIDs such as Carprofen or Meloxicam may be prescribed to reduce inflammation. These medications are safer for dogs than human NSAIDs. Joint supplements may also be considered to address certain deficiencies in the dog. Supplements such as glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, omega-3 fatty acid, green-lipped mussels, methylsulfonylmethane (MSM), and avocado soybean unsaponifiables (ASU) are some of the few that aid in joint health.
How to prevent lameness in dogs
For overweight dogs, weight management is crucial to alleviate strain on bones and joints. Dogs with arthritis or joint issues may benefit from joint supplements.
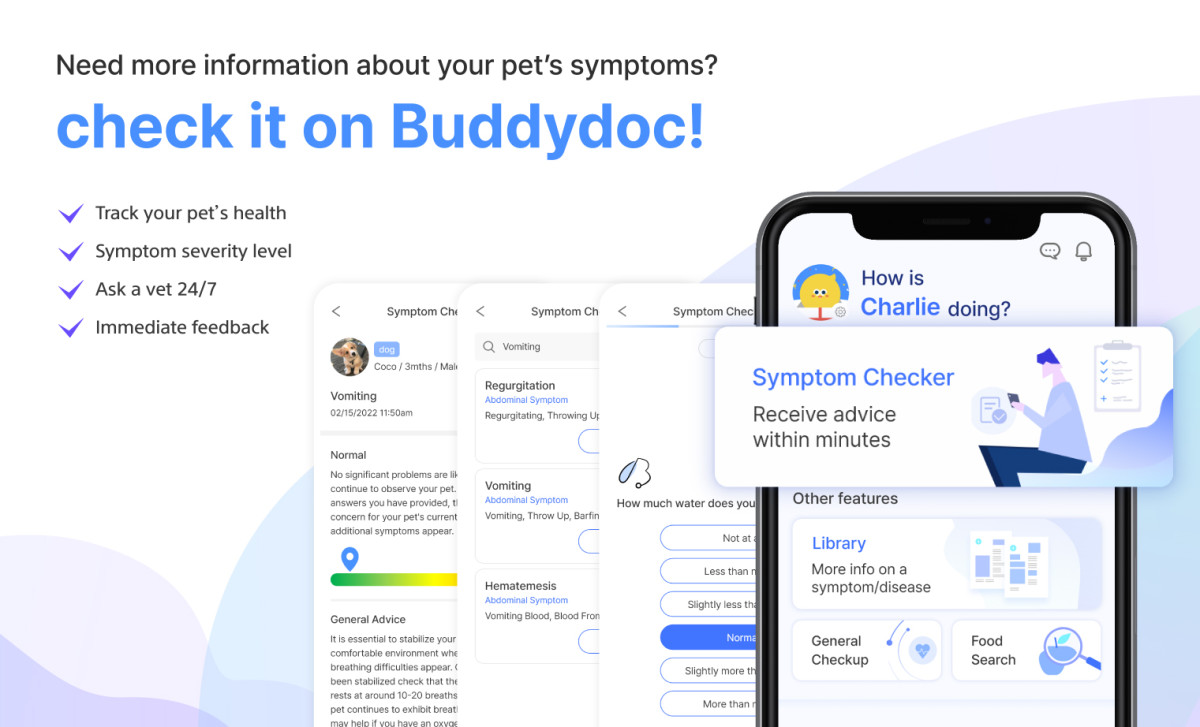
Find out more about your dog’s symptoms and diseases on the Buddydoc app!
The Buddydoc library is filled with everything you’d want to know about each symptom and disease your pet may experience. If you would like to find out more about the causes, signs, treatments, preventions, and more for your dog’s disease. Try out the Buddydoc app and search for your pet’s symptoms or diseases in the Buddydoc library.